Lynch syndrome (LS) is an inherited, cancer predisposition syndrome related to an elevated danger of colorectal, endometrial and different cancer sorts. Identifying people with LS permits entry to cancer danger administration methods confirmed to scale back cancer incidence and enhance survival.
However, LS is underdiagnosed and genetic referral charges are poor. Improving LS referral is advanced, and requires multisystem behaviour change. Although boundaries have been recognized, evidence-based methods to facilitate behaviour change are missing.
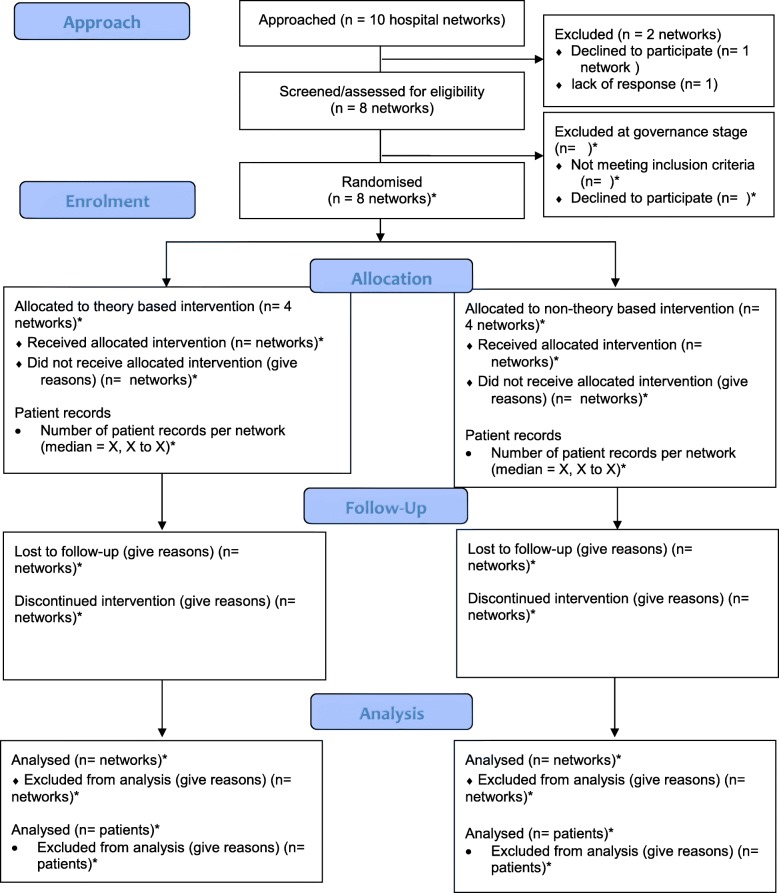
The intention of this examine is to evaluate the effectiveness of a theory-based implementation method towards a non-theory based method for improving detection of LS amongst Australian sufferers with colorectal cancer (CRC).
A two-arm parallel cluster randomised trial design shall be used to evaluate two equivalent, structured implementation approaches, distinguished solely by means of theory to determine boundaries and design focused intervention methods, to enhance LS referral practices in eight massive Australian hospital networks. Each hospital community shall be randomly allotted to a trial arm, with stratification by state. A educated healthcare skilled will lead the next phases at every website:
(1) undertake baseline medical follow audits, (2) type multidisciplinary Implementation Teams, (3) determine goal behaviours for follow change, (4) determine boundaries to change, (5) generate intervention methods, (6) assist workers to implement interventions and (7) consider the effectiveness of the intervention utilizing post-implementation medical knowledge. The theoretical and non-theoretical parts of every trial arm shall be distinguished in phases 4-5. Study outcomes embody a LS referral course of map for every hospital community, with analysis of the proportion of sufferers with risk-appropriate completion of the LS referral pathway inside 2 months of CRC resection pre and put up implementation.

Down syndrome (DS) is without doubt one of the most prevalent genetic problems in people. The use of recent approaches in genetic engineering and nanotechnology strategies in mixture with pure mobile phenomenon can modify the illness in affected individuals. We take into account two CRISPR/Cas9 programs to lower a particular area from brief arm of the chromosome 21 (Chr21) and exchange it with a novel designed DNA assemble, containing the important genes in chromatin transforming for inactivating of an additional Chr21.
This requires mimicking of the pure mobile sample for inactivation of the additional X chromosome in females. By technique of managed dosage of an acceptable Nano-carrier (a floor engineered Poly D, L-lactide-co-glycolide (PLGA) for integrating the related assemble in Trisomy21 mind cell tradition media and then in DS mouse mannequin, we might have the ability to consider the modification and the discount of the energetic additional Chr21 and in flip scale back substantial adversarial results of the illness, like mental disabilities. The speculation and examine search new insights in Down syndrome modification.